ターゲット話者音声認識のための空間自己教師あり学習
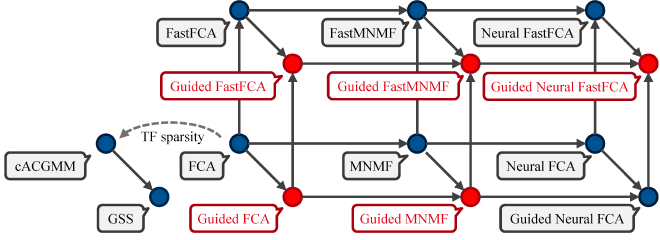
In this paper, we investigate spatial self-supervised learning for target speaker speech recognition. Neural separation models can be trained in a self-supervised manner by using only multichannel mixture signals. Such a framework is typically based on a physics-informed generative model, widely studied in blind source separation (BSS). Our study focuses on the application of spatial self-supervised learning for distant speech recognition (DSR). Multi-talker DSR systems often rely on a BSS method called guided source separation (GSS), which separates target speech utterances from multichannel mixtures and their speaker activities. Its performance, however, would be limited by its assumption that each time-frequency (TF) bin contains only one sound source or noise. To address this limitation, factor models have been studied by assuming each TF bin as a sum of all the sources. We investigate both the classic BSS and self-supervised methods based on factor models by evaluating them extensively on multiple different DSR scenarios in the CHiME-8 DASR challenge. We show that the classic BSS methods based on factor models suffer from initialization sensitivity, while self-supervised learning mitigated this problem and outperformed GSS.
| Title | Investigation of Spatial Self-Supervised Learning and Its Application to Target Speaker Speech Recognition |
| Authors | Yoshiaki Bando, Samuele Cornell, Satoru Fukayama, Shinji Watanabe |
| Conference | IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP) 2025 |
| Resources | PDF, GitHub |
Separation Excerpts of CHiME-8 DASR Benchmark #
Each block below shows log-magnitude spectrograms along with the separated audio for different guided factor models.
CHiME-6 #
Input

GSS

Guided FCA
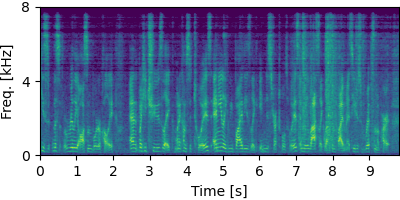

Guided MNMF
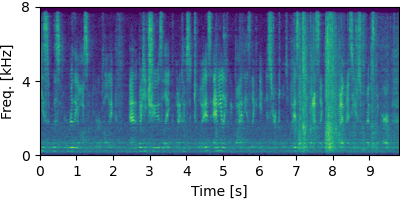

Guided FastFCA
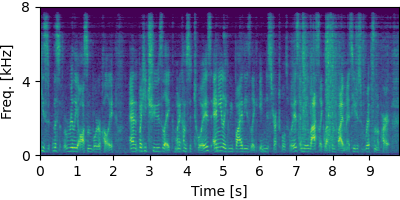

Guided FastMNMF
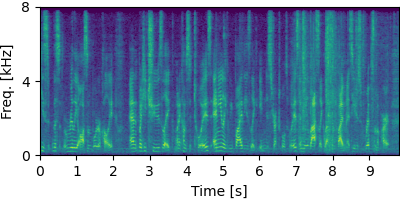

Guided Neural FastFCA (N=5)
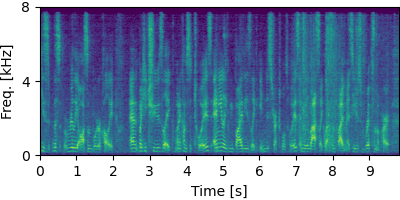

Guided Neural FastFCA (N=7)
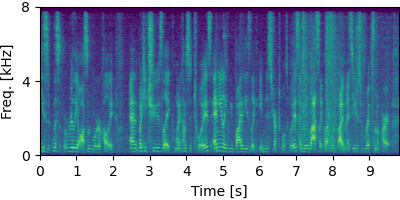

DiPCO #
Input
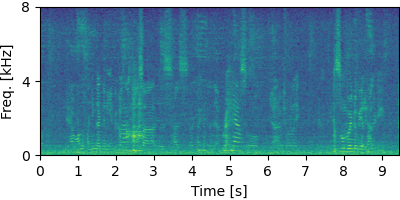

GSS
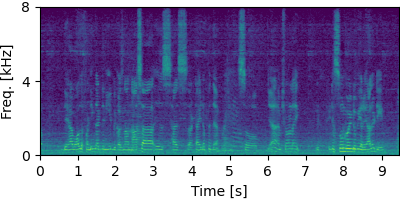

Guided FCA
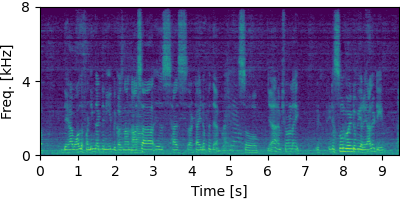

Guided MNMF
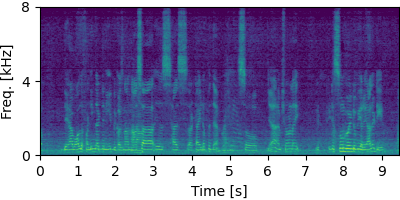

Guided FastFCA
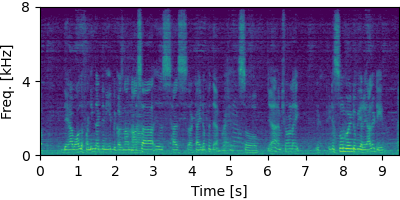

Guided FastMNMF
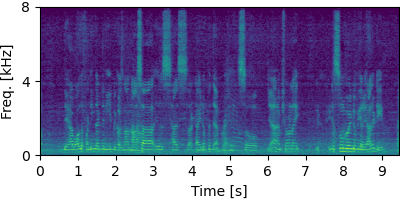

Guided Neural FastFCA (N=5)
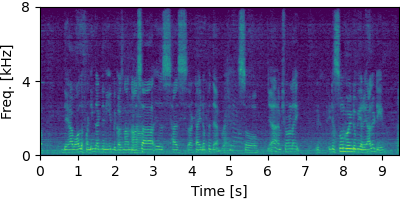

Guided Neural FastFCA (N=7)
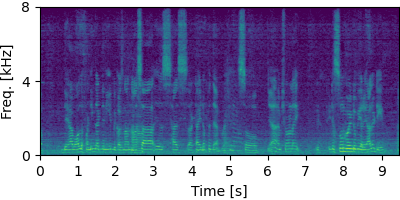

Mixer6 #
Input
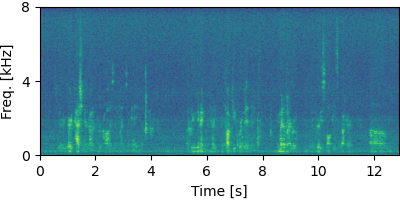

GSS
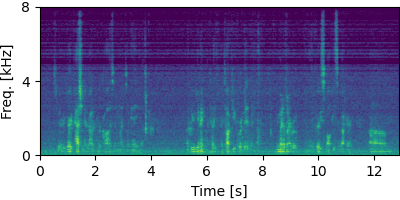

Guided FCA
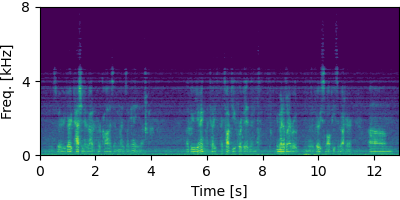

Guided MNMF
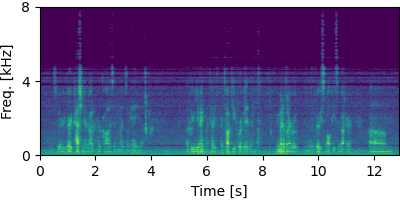

Guided FastFCA
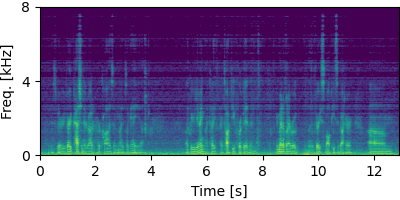

Guided FastMNMF
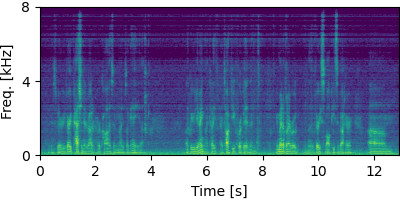

Guided Neural FastFCA (N=5)
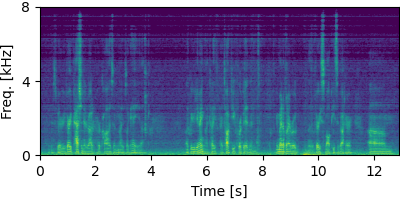

Guided Neural FastFCA (N=7)
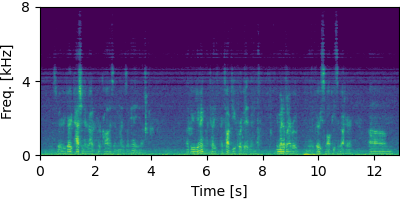

NOTSOFAR-1 #
Input
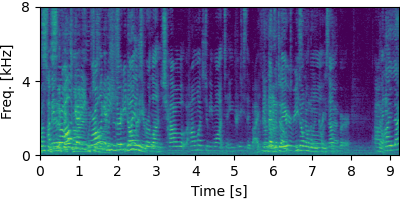

GSS
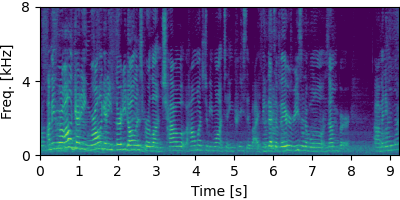

Guided FCA
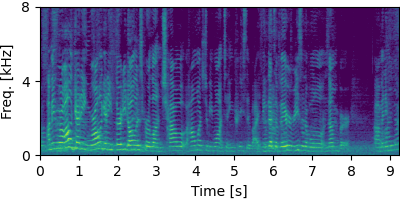

Guided MNMF
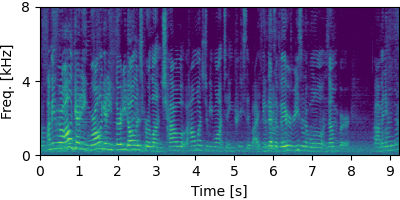

Guided FastFCA
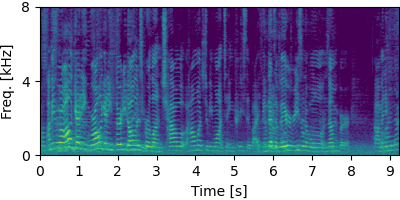

Guided FastMNMF
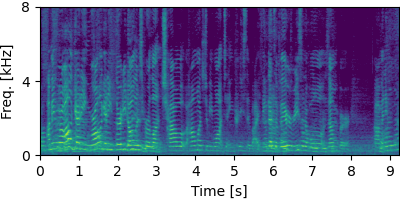

Guided Neural FastFCA (N=5)

Guided Neural FastFCA (N=7)